- Despite being historically volatile, Bitcoin is showing increasing resilience during macroeconomic stress, outperforming traditional equities (even the Magnificent 7) during recent market drawdowns
- Over longer time horizons, Bitcoin and other cryptoassets maintain low correlations with traditional assets like equities and bonds, enhancing portfolio diversification. However, intraday correlations reveal dynamic behaviour, especially during trading hours, emphasizing the importance of understanding temporal correlation shifts.
- With a long-term decline in realized volatility, growing scarcity, and rising institutional interest (including from central banks and sovereign wealth funds), Bitcoin is transitioning from a speculative asset to a potential reserve asset — even demonstrating superior hedging characteristics against US Treasuries compared to gold in specific scenarios.
Bitcoin has shown remarkable resilience amid the recent market turmoil created by the record increase in US economic policy uncertainty and the trade policies of the new Trump administration.
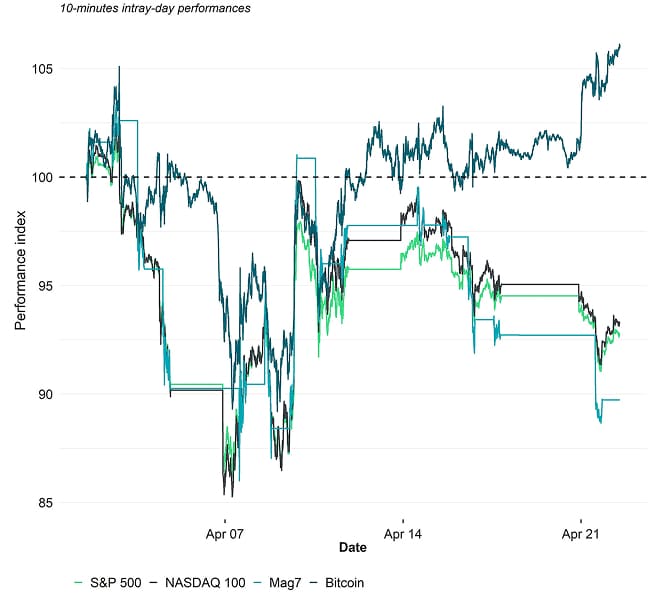
For instance, since April 2 -- the day US President Donald Trump issued an Executive Order implementing global tariffs -- the S&P 500, the NASDAQ 100, and every "Magnificent 7” (Mag7) stock has underperformed.
Meanwhile, Bitcoin (BTC) still managed to perform positively and outperform every Magnificent 7 stock:
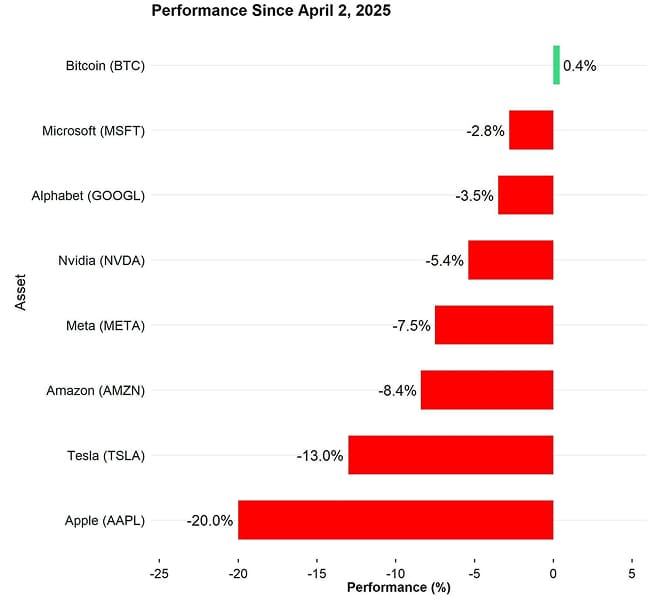
This is notable: As my colleague Matt Hougan pointed out in his April 14 CIO Memo, bitcoin has historically underperformed equities during periods of macro stress. This time we're seeing a different outcome, and it's sensible to ask: Why? Our thesis is that bitcoin is maturing as an institutional hedge asset, and is increasingly taking on the characteristics one would expect of such an asset: low correlations to stocks and bonds and declining volatility. Its transformation is not complete, but we see significant progress in the data.
Examining Correlations
Historically, correlations between major cryptoassets like Bitcoin and other assets have been quite low over long time horizons, as the following correlation matrix demonstrates.
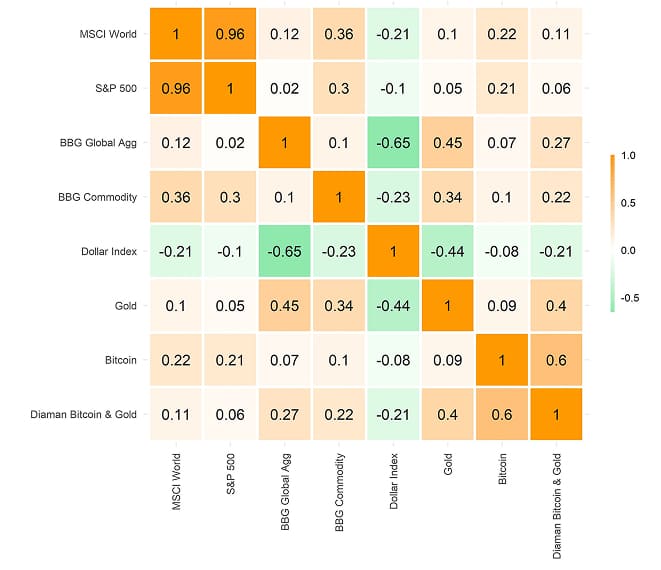
earliest data start: 2015-01-30; data as of 2025-04-15
That is one of the key reasons why cryptoassets can significantly enhance diversification in a multiasset portfolio and boost risk-adjusted returns over extended periods of time. (See our updated portfolio study here.)
Nonetheless, correlations are dynamic and can change significantly in the short term depending on the market regime.
In the short term, especially during risk-off periods - such as times of panic, volatility spikes, or liquidity crises - correlations between risky assets tend to spike. This heightened co-movement is largely driven by broad-based de-risking, where investors sell various assets indiscriminately, regardless of their underlying fundamentals.
Portfolio managers may also be forced to unwind positions or meet margin calls, leading to synchronized selling across markets. At the same time, a collective "flight to safety" can push all risk assets in the same direction-typically downward.
Over the long term, however, these correlations tend to weaken as fundamental drivers reassert themselves. Asset performance becomes more influenced by asset-specific trends, macroeconomic factors, earnings growth, valuations, and other idiosyncratic elements.
In essence, while short-term market behavior is often governed by sentiment and systemic reactions, long-term dynamics reflect the differentiated impact of economic and financial fundamentals.
In this context, the latest intraday correlations reveal that correlations between US equities and Bitcoin on a 10-minute basis during trading days have remained high.
That being said, they have started to decline more recently hinting at a potential decoupling between Bitcoin and US equities.
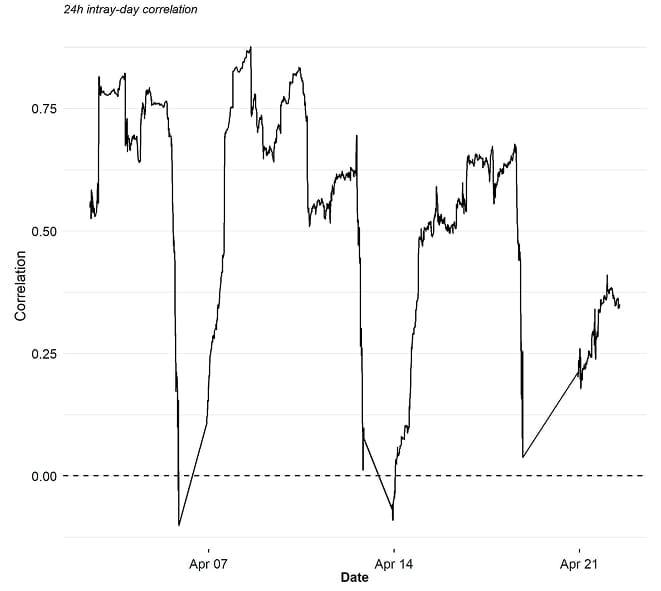
*based on 10-minutes intray-day closing bars
The implication is that while Bitcoin and other cryptoassets continue to be pressured by increasing macro risks and the US stock market, Bitcoin is demonstrating increasing resilience over the last couple of trading days.
Considering Volatility
In general, cryptoassets are still a relatively volatile asset class. That being said, as far as Bitcoin is concerned, realized volatility has been on a structural downtrend since its inception.
From an investment perspective, what Bitcoin is today is different from 10 years ago and will be different in the future.
Consider bitcoin's realized volatility during the most recent market Tariff Tantrum: While volatility has increased, it's dramatically lower than the peak volatility bitcoin experienced during previous halving epochs. Indeed, today's elevated volatility is close to the median volatility during the 2012-2016 era.
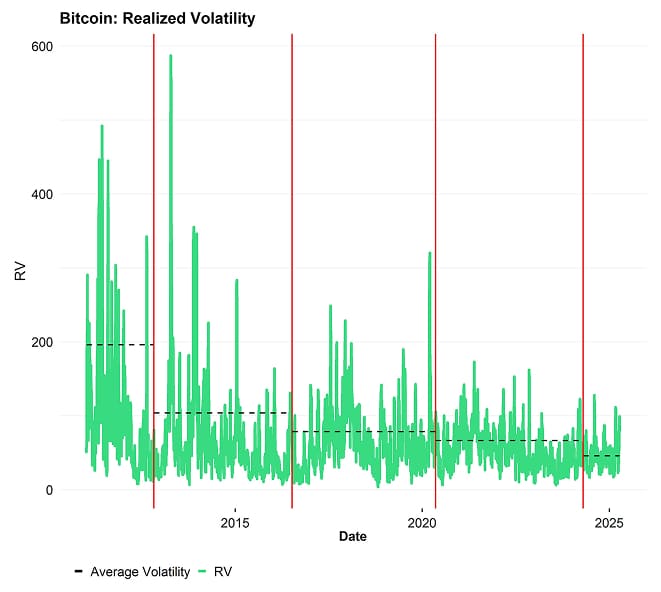
It is quite likely that this structural downtrend in volatility will continue in the future as Bitcoin is gradually evolving from a risky asset to a safe-haven asset over time.
We would note as well that, while market risk (read volatility) remains relatively high, Bitcoin essentially does not possess counterparty risk as a decentralized censorship-resistant asset. This is becoming increasingly relevant in a world of high fiscal debt and mounting sovereign default risks.
We have recently demonstrated that Bitcoin's “fair value” would already be higher than $200k today if it acted as a hedge against a basket of G20 sovereign bonds here.
Of note, although gold can be a better hedge against equity downside risks, Bitcoin is generally exhibiting a lower correlation to US Treasury bonds than gold and also better hedging characteristics during US Treasury down days than gold. This is what we dubbed “The Bitcoin-Bond Conundrum” which is also demonstrated here.
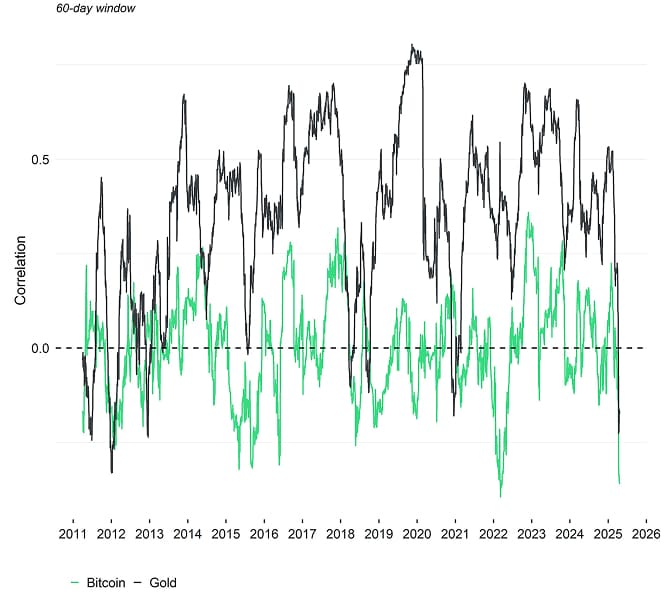
In fact, we have recently seen a significantly negative correlation between Bitcoin and US Treasury bonds on an intraday basis as well.
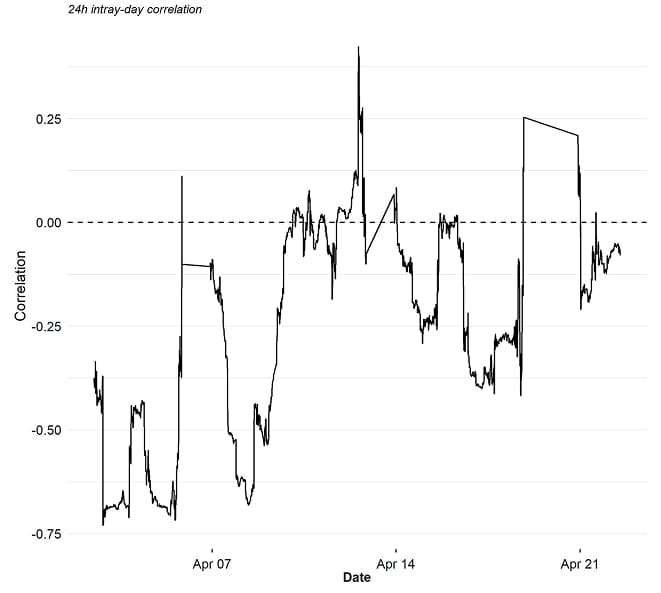
*based on 10-minutes intray-day closing bars
The implications of this are vast. Bitcoin may have important and complimentary “safe-haven” characteristics alongside gold.
It is no surprise that central banks and sovereign wealth funds are looking into Bitcoin as an alternative reserve asset. In fact, we could be at the cusp of a significant change in the market regime.
Bottom Line
- Despite being historically volatile, Bitcoin is showing increasing resilience during macroeconomic stress, outperforming traditional equities (even the Magnificent 7) during recent market drawdowns
- Over longer time horizons, Bitcoin and other cryptoassets maintain low correlations with traditional assets like equities and bonds, enhancing portfolio diversification. However, intraday correlations reveal dynamic behaviour, especially during trading hours, emphasizing the importance of understanding temporal correlation shifts.
- With a long-term decline in realized volatility, growing scarcity, and rising institutional interest (including from central banks and sovereign wealth funds), Bitcoin is transitioning from a speculative asset to a potential reserve asset — even demonstrating superior hedging characteristics against US Treasuries compared to gold in specific scenarios.
Important information:
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor does it constitute an offer or solicitation to buy financial products. This article is for general informational purposes only, and there is no explicit or implicit assurance or guarantee regarding the fairness, accuracy, completeness, or correctness of this article or the opinions contained therein. It is advised not to rely on the fairness, accuracy, completeness, or correctness of this article or the opinions contained therein. Please note that this article is neither investment advice nor an offer or solicitation to acquire financial products or cryptocurrencies.
Before investing in crypto ETPs, potentional investors should consider the following:
Potential investors should seek independent advice and consider relevant information contained in the base prospectus and the final terms for the ETPs, especially the risk factors mentioned therein. The invested capital is at risk, and losses up to the amount invested are possible. The product is subject to inherent counterparty risk with respect to the issuer of the ETPs and may incur losses up to a total loss if the issuer fails to fulfill its contractual obligations. The legal structure of ETPs is equivalent to that of a debt security. ETPs are treated like other securities.
