- Rising Sovereign Debt and Inflation Concerns: The U.S. has reached a record-high public debt of $36 trillion (123% of GDP), with debt growth accelerating post-2020. This, coupled with increasing fiscal deficits and geopolitical tensions, raises inflation risks and erodes trust in traditional financial systems. As a result, investors are seeking alternative stores of value such as Gold or Bitcoin, moving away from U.S. Treasuries.
- Bitcoin vs. Gold as Store-of-Value Assets: Bitcoin is increasingly seen as a "digital gold" due to its absolute scarcity (21 million max supply) and superior transferability compared to physical gold. While gold remains the primary safe-haven asset, Bitcoin’s technological advantages and adoption trends suggest it could challenge gold’s status over the long term.
- Diversification and Portfolio Hedging: Gold remains a strong hedge against market downturns, while Bitcoin is more volatile but offers higher returns during recoveries. Bitcoin also has a lower correlation with U.S. Treasuries, making it a valuable diversification tool, particularly as a hedge against sovereign defaults. A balanced allocation between Bitcoin and gold can optimize risk-adjusted returns.
Macro regime
[Bitcoin is] no different than what gold represented over thousands of years. It is an asset class that protects you.
- Larry Fink
The “Nixon shock” of 1971 has left the world on a fiat standard after the US government decided to de-anchor the US Dollar from gold which established US Treasuries as the de facto reserve asset.
50+ years into this economic experiment, the world has seen a significant increase in inflation rates and multiple systemic banking crises with detrimental consequences to the stability of the global financial system.
US total public debt has just recently surpassed 36 trillion USD which amounts to around 123% of GDP – the highest level ever recorded.
US: Total Public Debt
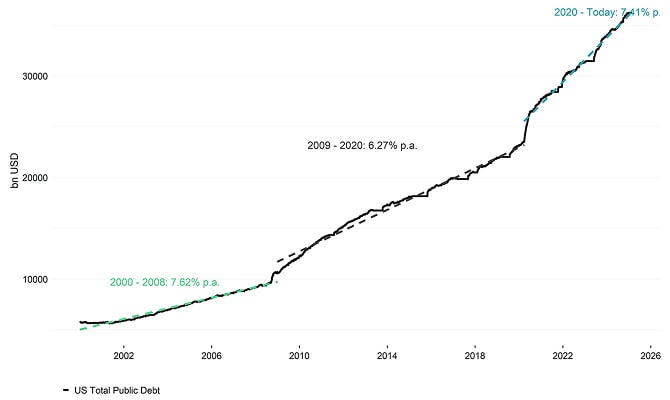
What is more is that the growth in US public debt appears to accelerate – since the beginning of September 2024, US total public debt has already grown by almost +1 trillion USD according to the latest data provided by Bloomberg. More specifically, total US public debt has been growing to the tune of 7.43% p.a. since April 2020 until today.
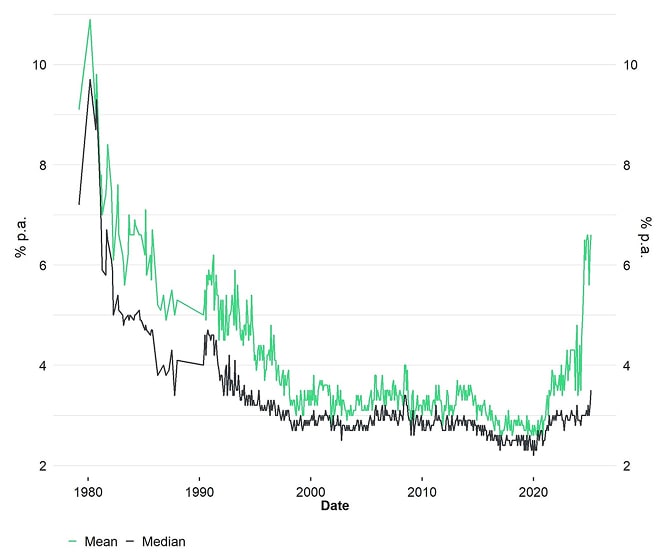
In addition, due to rising fiscal deficits, money supply growth rates have started to accelerate especially after the Covid crisis of 2020 necessitated an outsized fiscal and monetary response. However, this has led to a significant increase in inflation expectations and increases the risk of a high-inflation regime in the future.
University of Michigan: Inflation Expectations
Meanwhile, rising geopolitical tensions following the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022 and the freezing of Russian assets abroad, have led to a growing distrust in the established global monetary order and the safety of major sovereign bonds.
In general, rising geopolitical tensions also increase the likelihood of a high-inflation regime on account of a
- Potential hike in import tariff rates that increase import price inflation,
- Disruption in global supply-chains that is inflationary,
- Increase in commodity prices that affect food and energy price inflation.
It is no surprise that investors are looking for alternative hard assets to diversify their investments, in particular out of US Treasuries.
UST Foreign Holders Data by Country
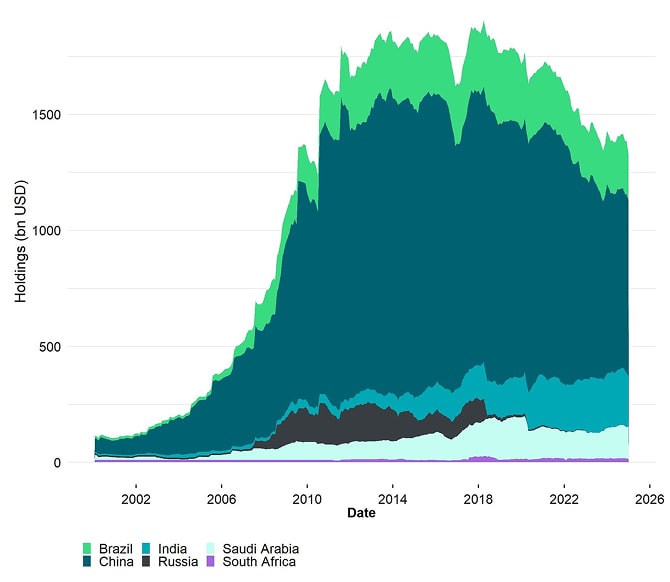
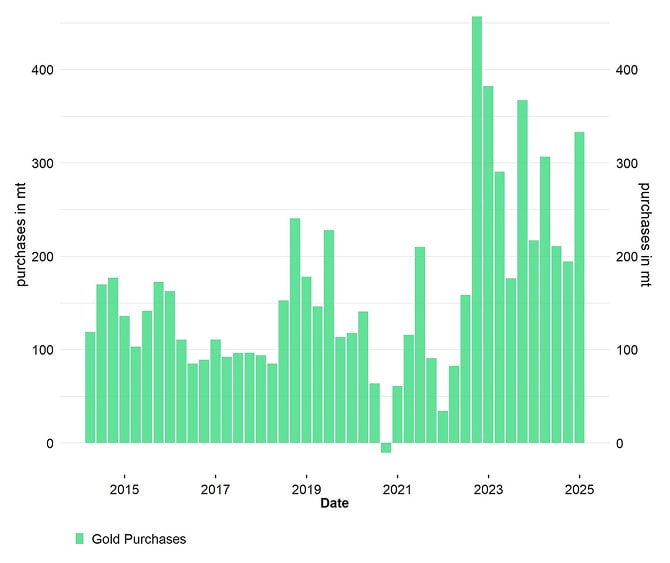
Major foreign holders like China have been reducing their US Treasury holdings in favour of traditional stores-of-value like Gold. In fact, the percentage of gold in international reserves has reclaimed the 2nd rank among reserve assets and has already overtaken the Euro. Gold purchases by major central banks have just recently hit the highest amount since 1967.
Central Bank Net Gold Purchases
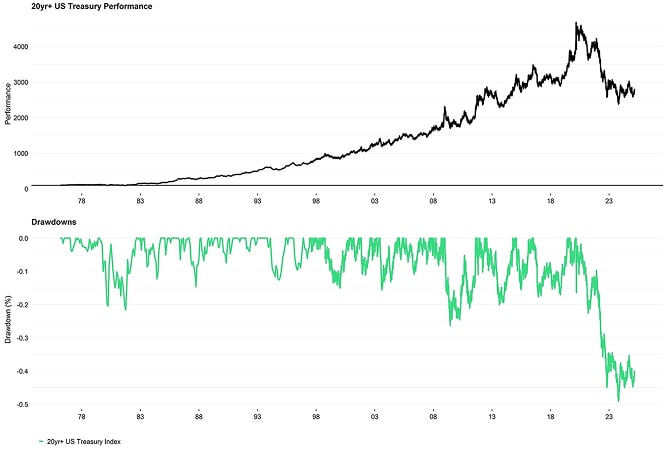
As a result, long-term US Treasury bonds have recorded their worst performance in history and are significantly underperforming Gold.
Meanwhile, Bitcoin is increasingly being adopted as an alternative store-of-value threatening to disrupt gold technologically over the long-term.
Central banks are officially looking to diversify their reserve assets into Bitcoin and the US and other countries are considering to establish a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve.
In fact, Bitcoin is already a 2 trillion USD asset which ranks it as the 7th most valuable single asset in the world – just between companies like Amazon and Saudi Aramco in terms of market cap. Bitcoin is often dubbed “digital gold” or “exponential gold” being caught between the exponential rise of technological adoption and absolute scarcity akin to gold.
But what is even special about Bitcoin?
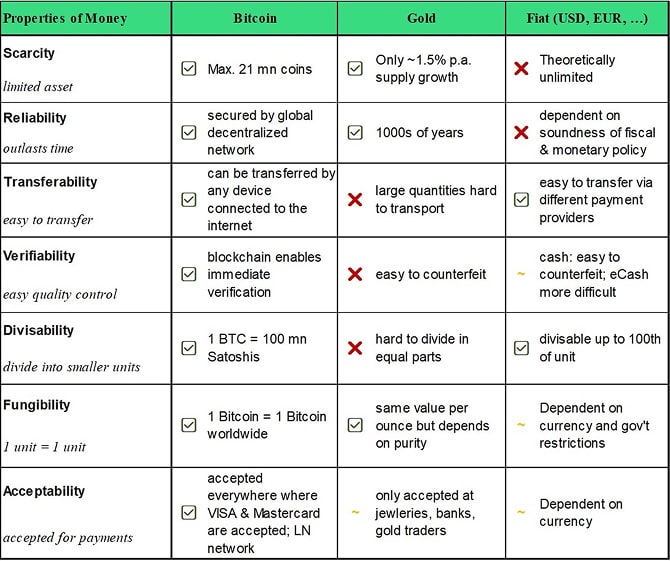
Differences between Bitcoin and Gold
Bitcoin is gold with teleportation built in.
- Vijay Boyapati
Gold is considered to be a good store-of-value because it can maintain a high level of purchasing power over time.
Experts speak about "temporal transferability".
The reason is that gold is relatively scarce due to its energy-intensive production which results in a low supply growth rate over time (around +1.5% p.a.).
In contrast, fiat monies like the US Dollar or the Euro permanently lose purchasing power over time but can be used to transfer value across large distances which is cumbersome with physical gold and incurs high transaction costs.
Experts speak of "spatial transferability”.
Gold did not manage to be widely used as a medium-of-exchange after 1971 mainly on account of its limited spatial transferability, which is why fiat monies started to dominate our day-to-day lives.
Bitcoin has often been compared to gold due to its energy-intensive proof-of-work algorithm which verifies transactions and creates the new supply of bitcoins.
Bitcoin can be very volatile in the short term. However, due to its low supply growth rate (+0.8% p.a.) and absolute scarcity (max 21 million bitcoins), it is also considered to be a good store-of-value over long periods of time with an increasing purchasing power.
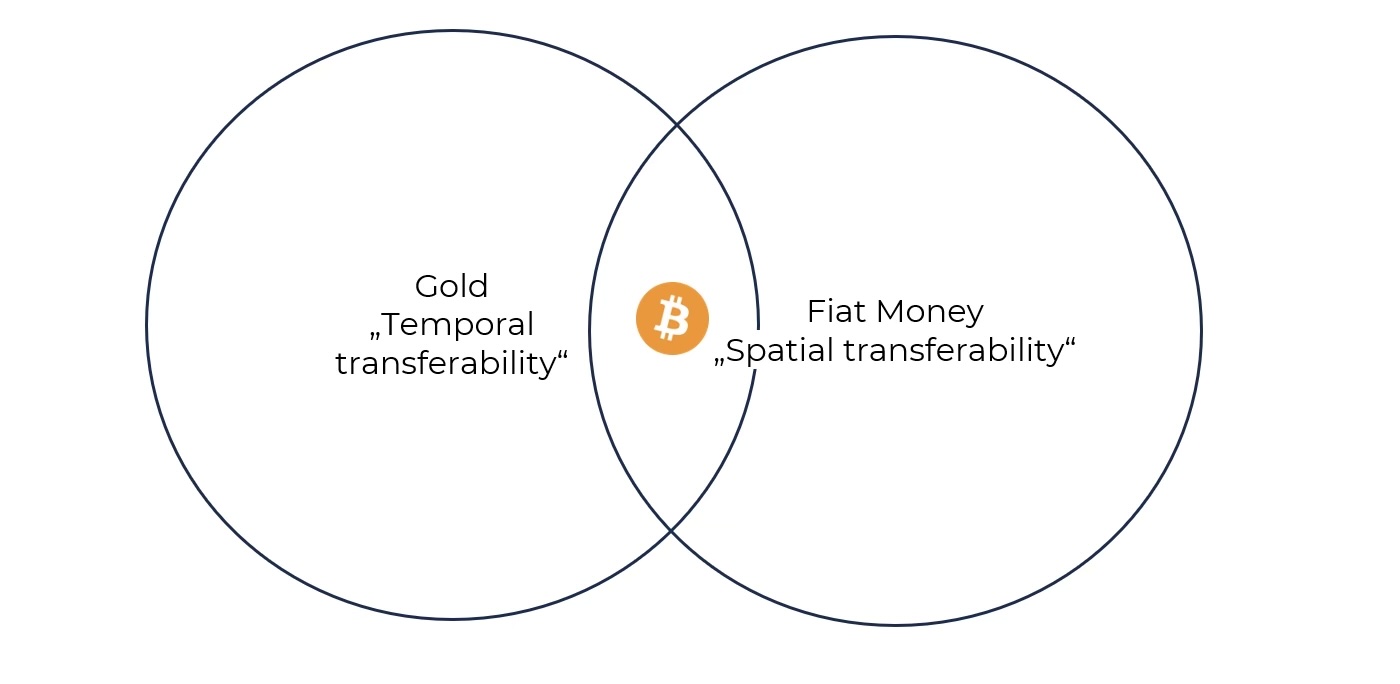
At the same time, due to its digital nature, and superior transferability, divisibility, and verifiability, Bitcoin also exhibits a high degree of spatial transferability like fiat monies.
In other words, Bitcoin combines the temporal transferability of gold with the spatial transferability of fiat monies.
Thus, due to its technological superiority, it is quite likely that Bitcoin could disrupt Gold over the long term. In fact, our official prediction is that Bitcoin could already reach gold’s market cap by the end of this decade.
That being said, over the short- to medium-term gold is likely to maintain its status as a the prime safe-haven asset while the ongoing adoption and changing character of Bitcoin makes it the closest contender for that status over the long term.
Bitcoin as an alternative hedge against sovereign default and inflation?
Government risk premia have been rising for major sovereign issuers like the US, UK, and France, as reflected in their increasing swap spreads. Consequently, investors are seeking alternative stores of value to hedge against counterparty risks.
Gold has traditionally served this purpose, with central banks still holding substantial reserves.
10-year sovereign swap spreads
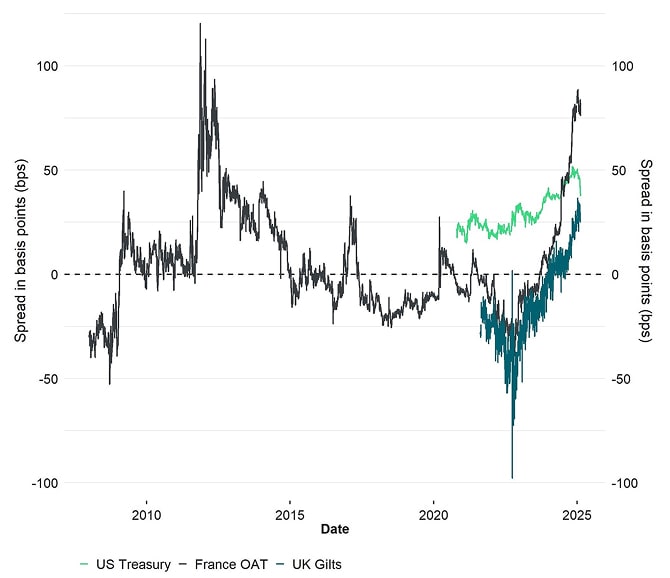
Bitcoin presents a compelling digital alternative.
Unlike sovereign assets, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized, trust less network of nodes and miners that validate transactions and enforce consensus rules. This eliminates counterparty risk, as Bitcoin holdings are not intermediated by a central entity and remain resistant to censorship or confiscation.
Foss (2021) suggests that itcoin can act as "portfolio insurance" against sovereign bond defaults. Under a model linking Bitcoin’s value to the default risk of G20 sovereign bonds—currently valued at $69.1 trillion with an average 10-year default probability of 6.2%—Bitcoin's "fair value" could already be in the thousands per BTC. In an extreme scenario where all G20 bonds default, this model estimates a theoretical Bitcoin price of $3.5 million per BTC. These figures exclude unfunded liabilities, which could push valuations even higher. Read the detailed analysis here.
While large-scale sovereign defaults remain unlikely in the short term, historical patterns suggest they are not rare. Reinhart & Rogoff (2009) documented around 320 sovereign external debt defaults since 1800, with governments often inflating away domestic debt rather than defaulting outright.
Ahmed et al. (2024) provide further evidence of Bitcoin’s hedge properties, showing a correlation between rising sovereign default risk and increased crypto adoption in emerging markets. With its decentralized, counterparty risk-free nature and growing scarcity, Bitcoin remains a compelling hedge against sovereign financial instability.
Given Bitcoin’s supply growth of just 0.9% per year, it stands to benefit from both default scenarios and high-inflation environments.
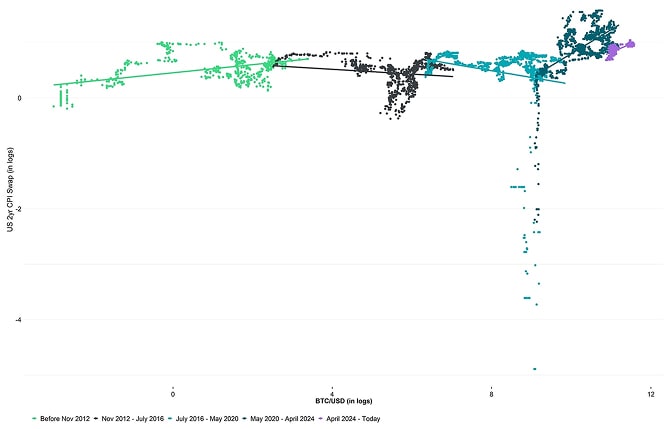
In fact, we are seeing an increasing sensitivity of Bitcoin’s price to market-based US inflation expectations with an increasing level of scarcity.
Bitcoin vs US 2-year CPI Swaps
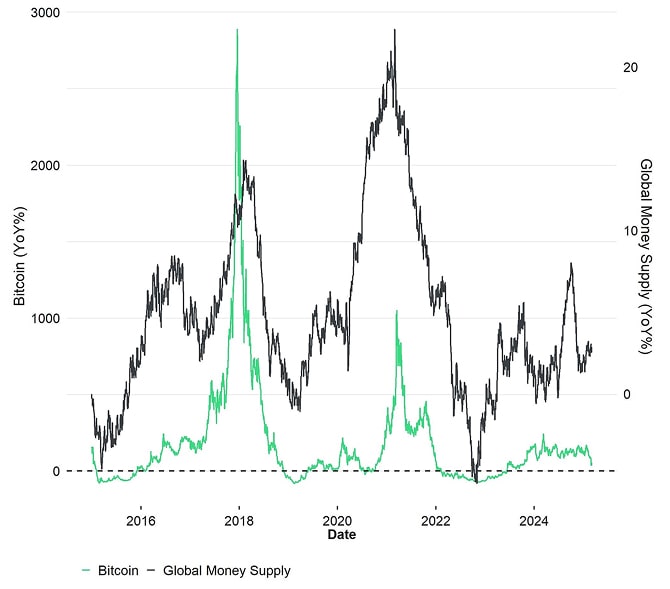
Therefore, it is also not surprising that Bitcoin tends to cycle with the ebbs and flows of global money supply expansion and contraction.
In fact, due to its absolute scarcity and low supply growth relative to fiat currencies, Bitcoin may be the best barometer for global monetary dilution that we have.
Bitcoin vs Global Money Supply Growth
Bitcoin, Gold or Both?
Both assets have their advantages and disadvantages and the answer to that question may ultimately depend on your risk tolerance.
While small Bitcoin allocations can boost (risk-adjusted) portfolio returns significantly, gold allocations can reduce the overall risk profile of your multi-asset portfolio in terms of drawdown and volatility as highlighted here.
In terms of portfolio hedge, Gold continues to exhibit a very good hedge during risk-off market environments. In fact, on average, gold has shown a positive performance when the S&P 500 dropped by more than -2% in a single day as highlighted here.
In contrast, Bitcoin has generally shown a negative performance (-2.6%) during these adverse market environments while gold managed to provide a true downside hedge (+0.1%) with an average decline of the S&P 500 by -3.1% during these down days.
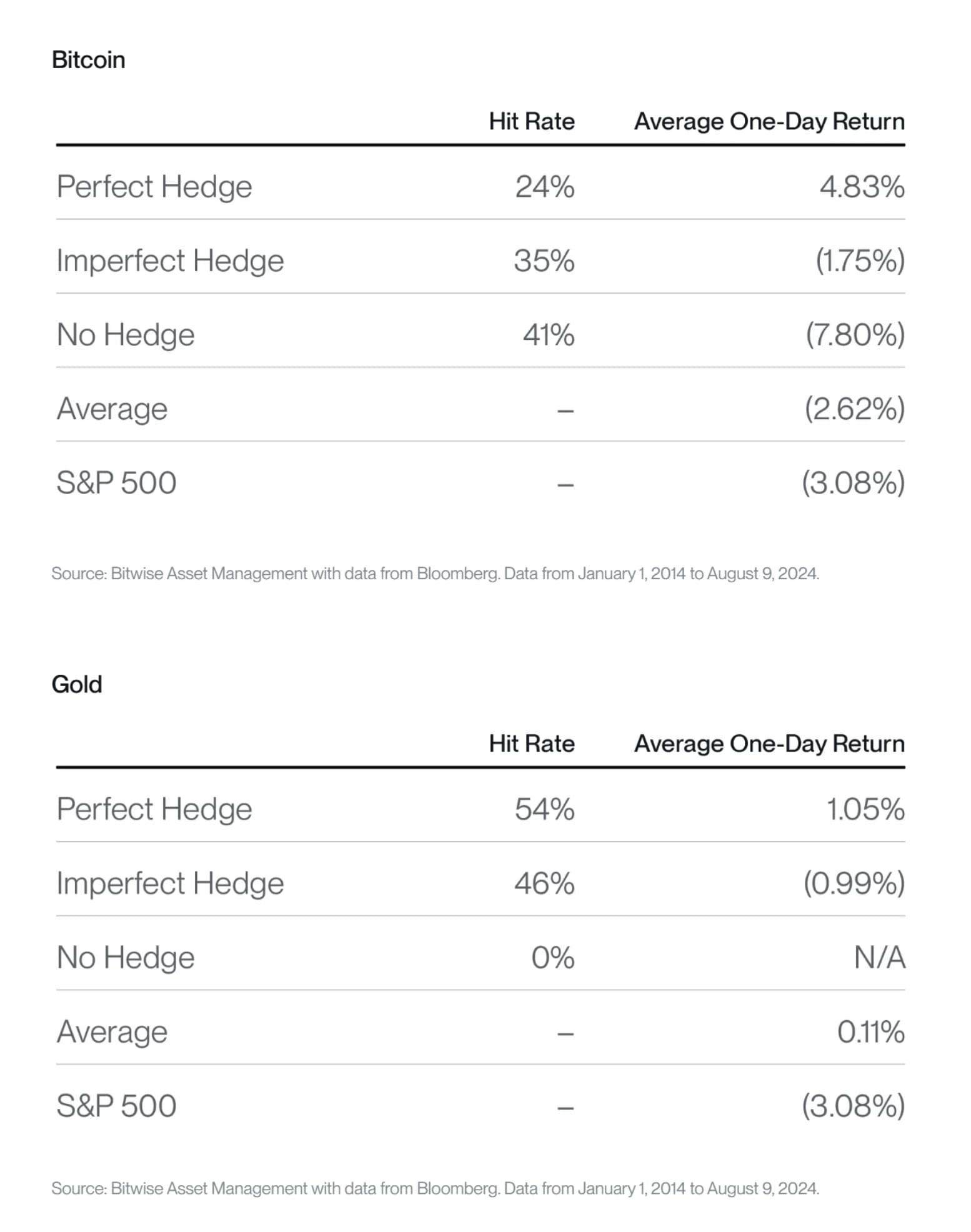
In other words, Bitcoin continues to be a “risky asset” in terms of market risks while gold can act as true downside hedge during adverse market conditions.
That being said, Bitcoin has recovered very strongly following historical US stock market corrections with an average performance of +189.6% after 1 year following larger stock market corrections. In contrast, gold has averaged only +7.9% after 1 year.
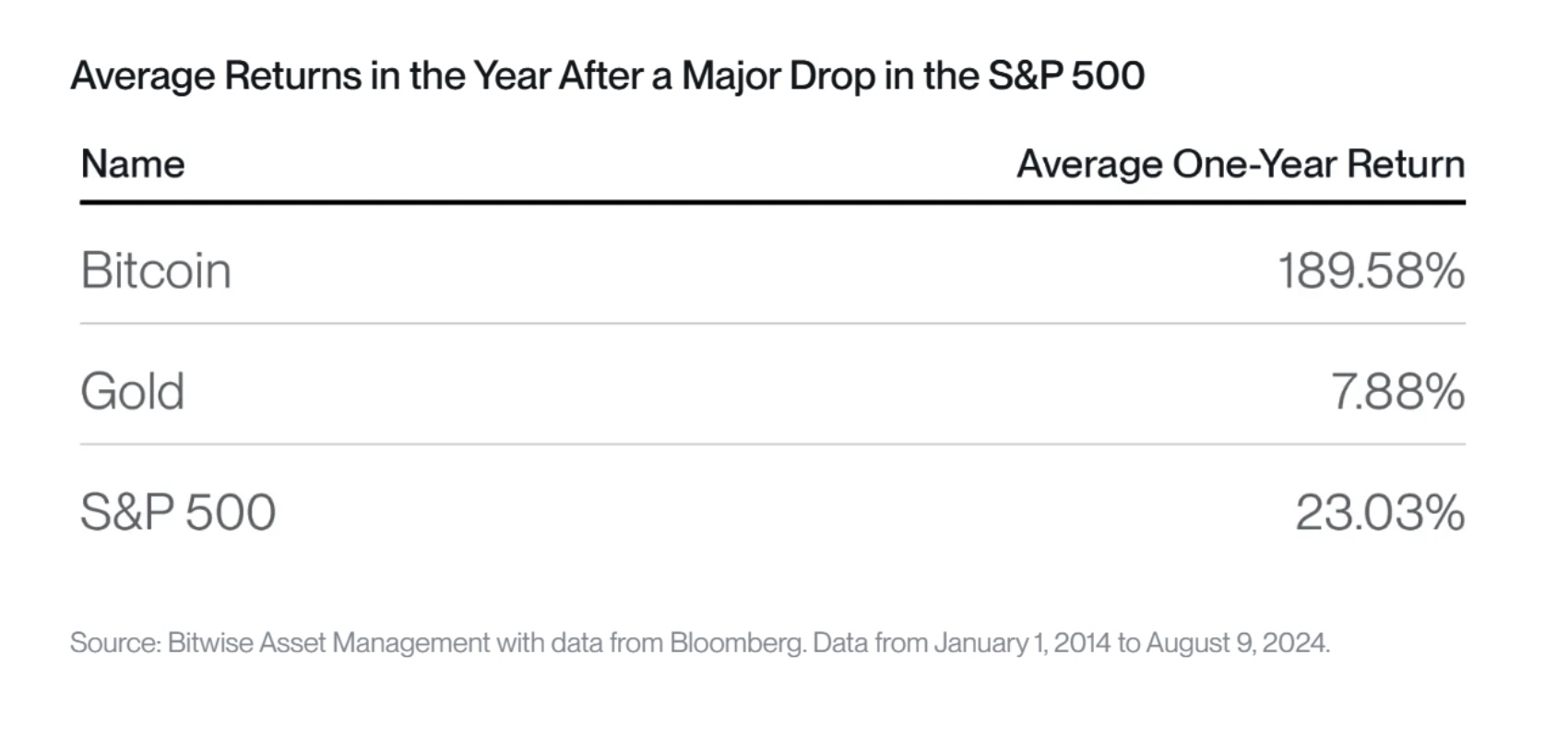
To put simply, Gold continues to be the better downside hedge but Bitcoin should be the preferred asset during recoveries.
Hence, a dynamic allocation strategy could be beneficial in this regard, both in the short-term (tactical allocations) and long-term (structural shifts from gold to Bitcoin).
That being said, there is an interesting diversification aspect about Bitcoin that is often disregarded in a broader portfolio context. Compared to gold, Bitcoin generally exhibits a significantly lower correlation to US Treasury bonds. This is both evident on a rolling basis and full-sample basis.
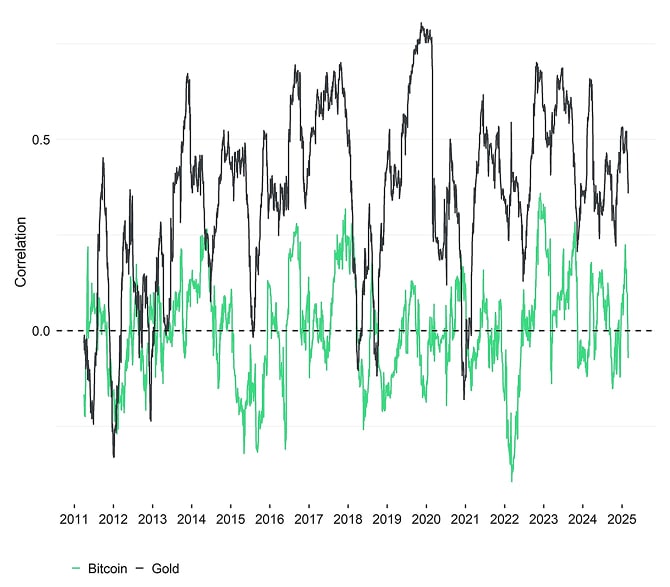
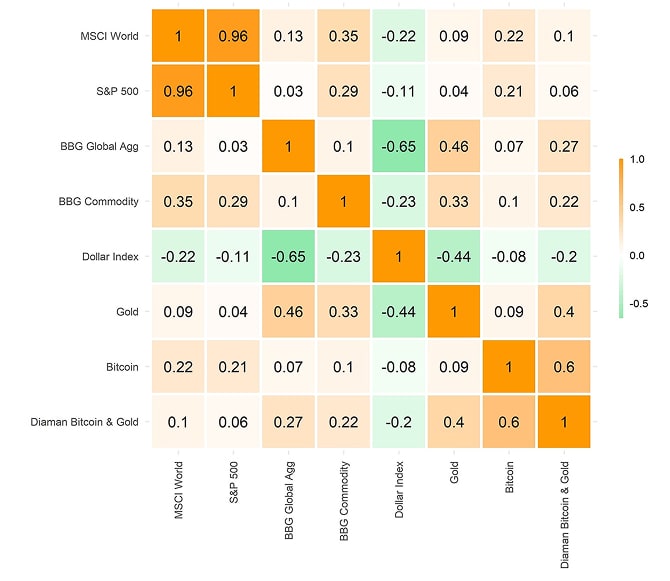
earliest data start: 2015-01-30; data as of 2025-02-28
In other words, while gold can offer a good hedge and diversification for the equity bucket within a multi-asset portfolio, Bitcoin offers more favourable diversification benefits for the bond bucket of the multi-asset portfolio.[1]
This is even more interesting in the context of Bitcoin representing a potential “portfolio insurance” against a sovereign default as outlined above.
However, there is a case to be made to own both assets within a portfolio. The bigger question is:
How to allocate between Bitcoin and Gold?
Common risk-budget strategies assign portfolio weights inversely to realized volatility, often using standard deviation as a key measure.
However, standard deviation fails to capture market directionality, meaning both rising and declining trends can have the same volatility despite differing investor perceptions.
The Ulcer Index, introduced by Martin Peter in 1987[2], measures drawdowns from previous highs, calculated as:
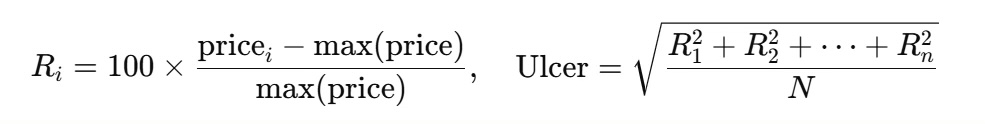
The Ulcer Index offers a clearer view of market trends. Though not academically recognized, it relates losses to recovery time, allowing for more dynamic and trend-sensitive portfolio construction compared to risk parity.
The Ulcer Index allows for a procyclical allocation over time. This allows for a dynamic allocation to both Bitcoin and Gold over time that mitigates tail risks but also allows investors to participate in strong trends.
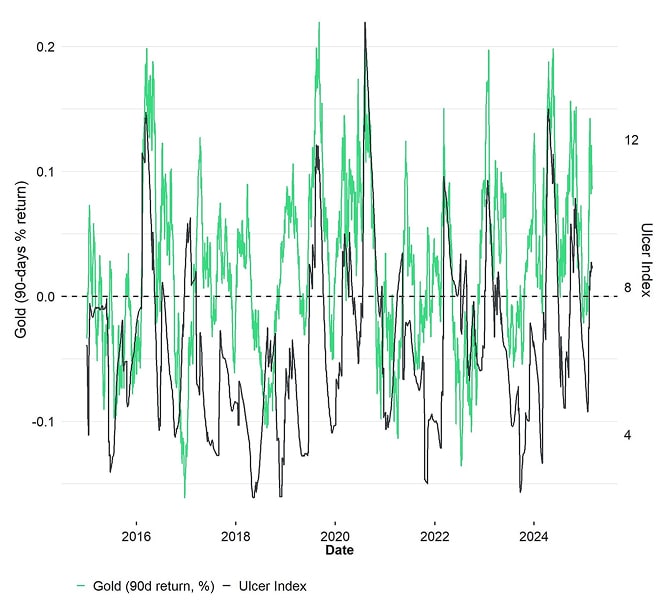
The Ulcer Index is also applied in the risk-budgeting of the Damian Partner Bitcoin & Gold Index, effectively keeping realized volatility low while still capturing Bitcoin's high returns:
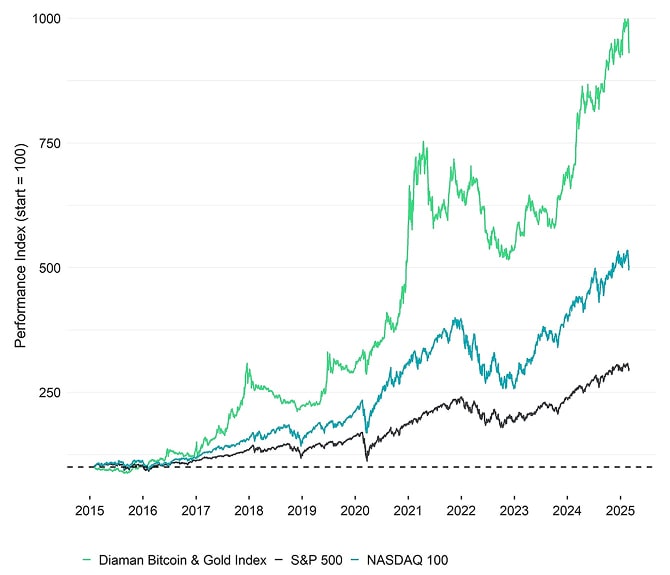
Performance: Bitcoin + Gold vs US equities
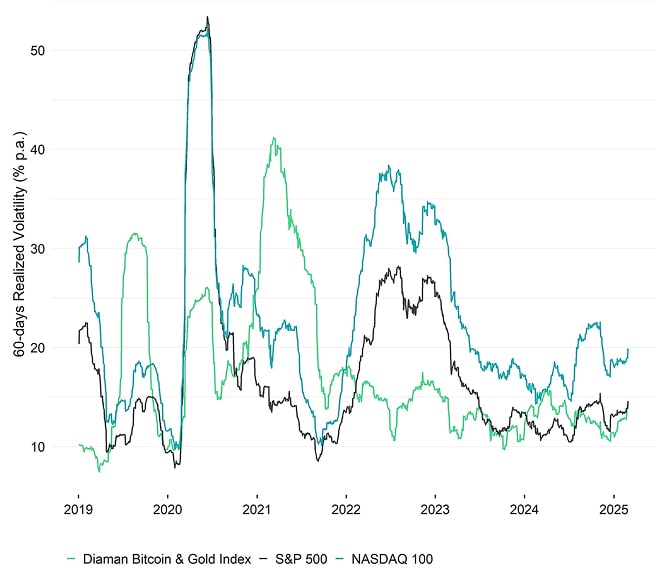
Volatility: Bitcoin + Gold vs US equities
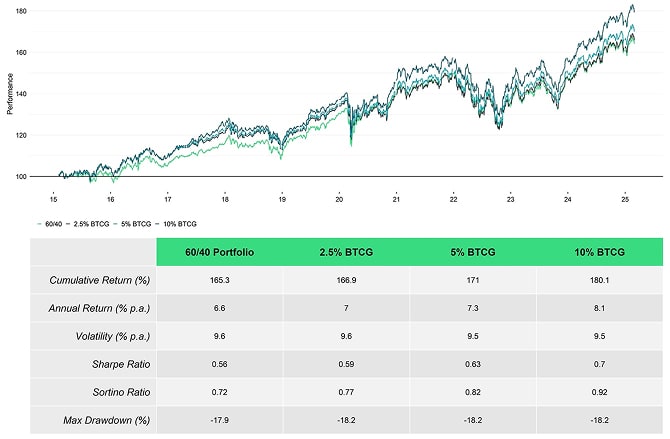
That’s why an inclusion of Bitcoin and Gold can significantly boost risk-adjusted portfolio returns without jeopardizing the overall risk characteristics of the portfolio.
In fact, portfolio volatility and max drawdown remain almost unaffected by increasing allocations to our Bitcoin & Gold Index.
[1] Besides, our quantitative analyses reveal that Bitcoin has also been a great hedge against gold drawdowns and vice versa which support the rationale of allocating to both assets in a portfolio.
[2] See Martin, P., & McCann, B. (1989). The investor's guide to Fidelity funds: Winning strategies for mutual fund investors. Wiley.
Bottom Line
- Rising Sovereign Debt and Inflation Concerns: The U.S. has reached a record-high public debt of $36 trillion (123% of GDP), with debt growth accelerating post-2020. This, coupled with increasing fiscal deficits and geopolitical tensions, raises inflation risks and erodes trust in traditional financial systems. As a result, investors are seeking alternative stores of value such as Gold or Bitcoin, moving away from U.S. Treasuries.
- Bitcoin vs. Gold as Store-of-Value Assets: Bitcoin is increasingly seen as a "digital gold" due to its absolute scarcity (21 million max supply) and superior transferability compared to physical gold. While gold remains the primary safe-haven asset, Bitcoin’s technological advantages and adoption trends suggest it could challenge gold’s status over the long term.
- Diversification and Portfolio Hedging: Gold remains a strong hedge against market downturns, while Bitcoin is more volatile but offers higher returns during recoveries. Bitcoin also has a lower correlation with U.S. Treasuries, making it a valuable diversification tool, particularly as a hedge against sovereign defaults. A balanced allocation between Bitcoin and gold can optimize risk-adjusted returns.
Important information:
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor does it constitute an offer or solicitation to buy financial products. This article is for general informational purposes only, and there is no explicit or implicit assurance or guarantee regarding the fairness, accuracy, completeness, or correctness of this article or the opinions contained therein. It is advised not to rely on the fairness, accuracy, completeness, or correctness of this article or the opinions contained therein. Please note that this article is neither investment advice nor an offer or solicitation to acquire financial products or cryptocurrencies.
Before investing in crypto ETPs, potentional investors should consider the following:
Potential investors should seek independent advice and consider relevant information contained in the base prospectus and the final terms for the ETPs, especially the risk factors mentioned therein. The invested capital is at risk, and losses up to the amount invested are possible. The product is subject to inherent counterparty risk with respect to the issuer of the ETPs and may incur losses up to a total loss if the issuer fails to fulfill its contractual obligations. The legal structure of ETPs is equivalent to that of a debt security. ETPs are treated like other securities.
 En
En  It
It  De
De 