VCs pile in on Crypto Winter, exceed €13bn in 2022
It has become something of a meme that bear markets are time for founders to build, away from the distraction of soaring token prices. But it's true. When everything is exploding, as markets did in 2021, there is an incredible pressure on development teams to release products that may not be battle-tested. But now that digital asset markets are not so heavily hyped, VCs and fundraisers are piling billions of euros into the next wave of Web3, DeFi and crypto startups.
The total poured into crypto startups worldwide in 2022 so far exceeds €13.6bn. That means despite Crypto Winter taking full effect and investors suffering the deepest bear market in recent memory, institutional investors are on course to surpass 2021, thereby building out a massive crypto ecosystem.
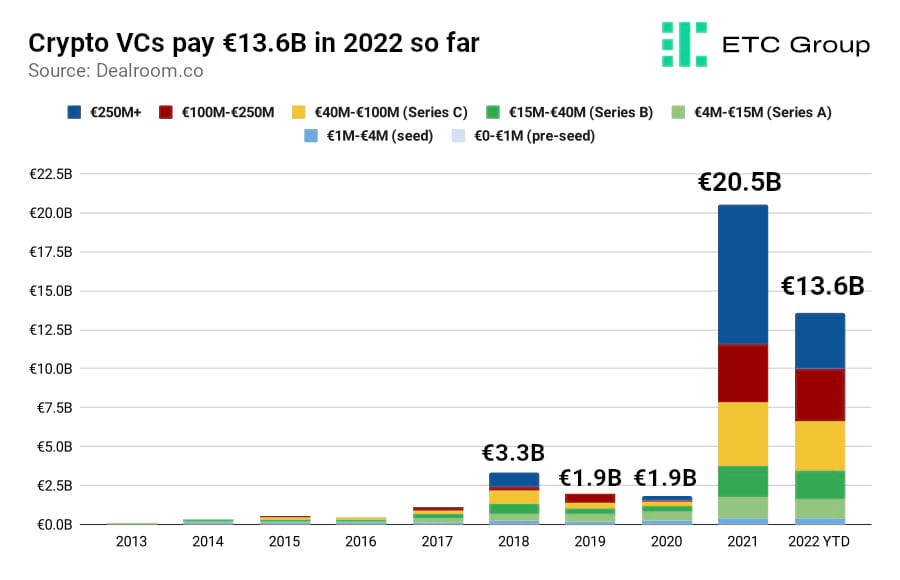
2018 was the first year in which VCs made a €250m+ capital injection in any crypto company. But it was also the start of the most recent Crypto Winter. Venture funding in crypto dropped from €3.3bn in 2018 to €1.9bn in both 2019 and 2020.
In Europe, the recent picture remains particularly bullish. Fintech funding data via Dealroom, as reported by Sifted, shows that European crypto and DeFi startups won $452m across 28 funding rounds in Q3 2022.
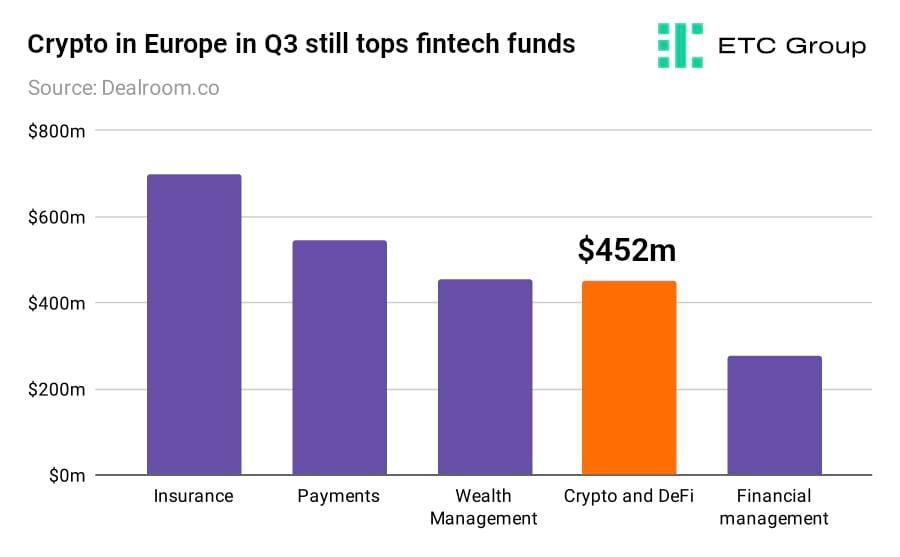
Crypto companies took up the lion's share of the quarter's largest rounds, and $100m seemed to be VCs' magic number. Blockchain protocol RubiX Network, digital wallet Safe (previously Gnosis Safe) and blockchain network 5ire all raised $100m from mostly crypto-focused funds, while blockchain startup Fuel Labs raised $80m,
the fintech-focused news site reported.
This takes the total invested in crypto startups in Europe to nearly $2bn for the year. $2.8bn was invested into crypto startups in Europe in 2021. So even with markets 55% lower than their all time high in November of last year, it is encouraging to see such continued fascination from private equity and capital allocators.
Gnosis was originally an open source prediction market built on Ethereum. In recent years developers have switched to focusing on building out the wider Ethereum ecosystem, specifically supporting the Merge in mid-September, and switching to custody more recently, noting that they now manage almost $40bn in Ethereum-based digital assets.
It has become clear that those businesses with a foot in Web2 - who have experience in building legal structures, tooling, libraries and devkits - and yet want to build with a decentralised Web3 mindset, will be the biggest winners of the next cycle.
US universities invest in Bitcoin Lightning Network
In 2018, when the world's richest university endowments started to invest in crypto funds, it was heralded as the switchover point when digital assets became truly mainstream.
Then in 2020, those same universities began buying Bitcoin directly.
Now the highest-capitalised endowments are starting to invest in the infrastructure behind cryptocurrencies, in the latest signal that institutions are seeing the generational value in blockchain technologies.
The Bitcoin payments app Strike reported in late September it had scored a $80m fundraising round from VC firm Ten31, joined by the University of Wyoming and Washington University in St. Louis. The latter academic institution is the 10th largest in the United States, with an asset value of $13.7bn.
Strike bears similarities to Visa and Mastercard but instead settles transactions using Bitcoin's Lightning Network.
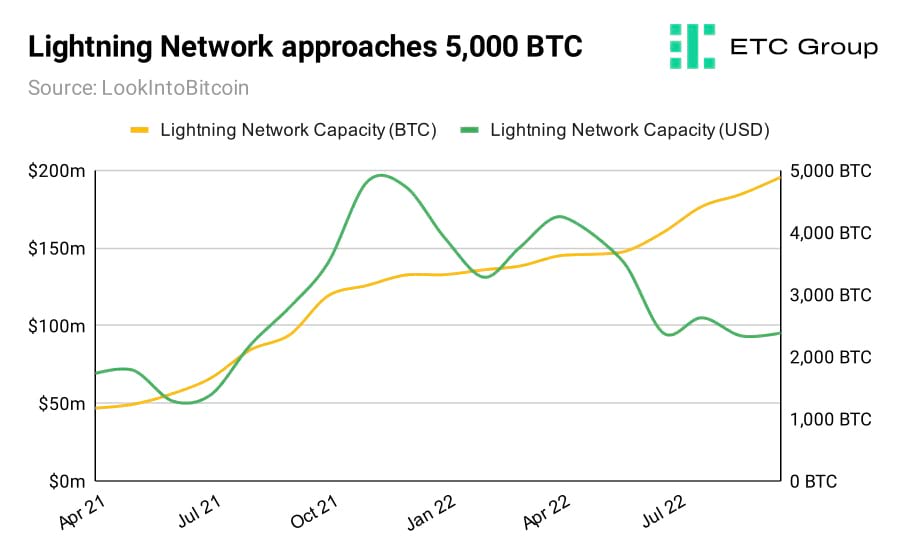
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain to make it more scalable.
Because of the sheer number of transactions that take place on the Bitcoin network, it can become slow and expensive to use. The Lightning Network service pulls computationally-intensive transaction processing away from the main Bitcoin blockchain, reducing fees to a mere fraction of a cent.
The Lightning Network is one of the first applications to use smart contracts on Bitcoin.
Strike became a lightning rod of attention last year when it partnered with El Salvador to roll out digital wallets to support Bitcoin transactions in the country.
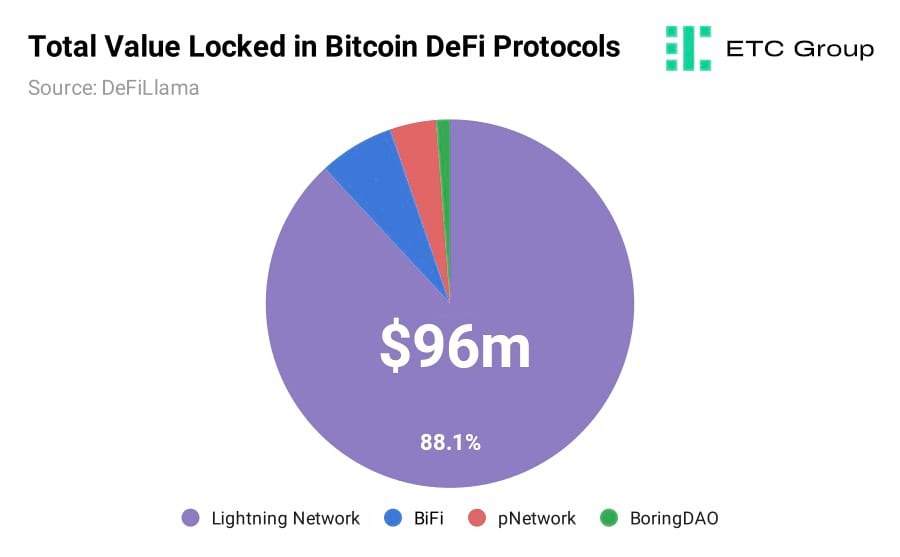
The capacity of the Lightning Network has grown at pace over the past year, independent of the price volatility of the underlying asset. Still, its $96 million capacity (green line in chart above) currently pales in comparison to the dollar value of tokenised Bitcoin sitting in DeFi ecosystems powered by smart contract blockchains like Ethereum.
$578 million of Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) and $340 million of cWBTC can be found on DeFi protocols like Aave and Compound alone. Ethereum is the home of DeFi with a TVL of $31 billion. This contrasts with the $110 million locked in Bitcoin DeFi protocols. The Lightning Network accounts for 88% of Bitcoin DeFi.
Endowments are an aggregation of the pools of capital held by universities, and are used to finance anything from scientific research to strategic investments in emerging technologies.
According to the latest available figures, United States institutions have over $675bn in endowments. Harvard University is the largest with over $40bn. Asset managers are tasked with investing on very long timeframes, given that such investments need to support these institutions in their ability to grow on a generational scale.
Cosmos debuts new whitepaper to boost ATOM
The modular app-specific blockchain is going to be a key narrative for markets in 2023. Instead of Layer 1 chains that do everything, it is highly likely that more blockchains designed for specific purposes will emerge.
As it stands today, individual blockchains generally act as their own closed ecosystems, making it difficult for them to interact with other blockchains. Without external bridges, the assets and value on these chains tends to stay locked inside them.
Enter Cosmos, a new type of blockchain architecture whose main aim is to create interoperability between hundreds or even thousands of parallel, independent blockchains.
In direct opposition to Ethereum, where every dapp built on the network competes for the same block space, Cosmos is built in a different way.
Instead of being a single blockchain where every application ‘lives', it is a network of many blockchains, each customised for their particular application. But its native token ATOM has not always been the beneficiary of this structure. As such - and despite creating a huge ecosystem of NFT marketplaces, gaming and DeFi blockchains that have transacted $21 billion between them in 2022 so far - the ATOM token value has long lagged behind its rivals.
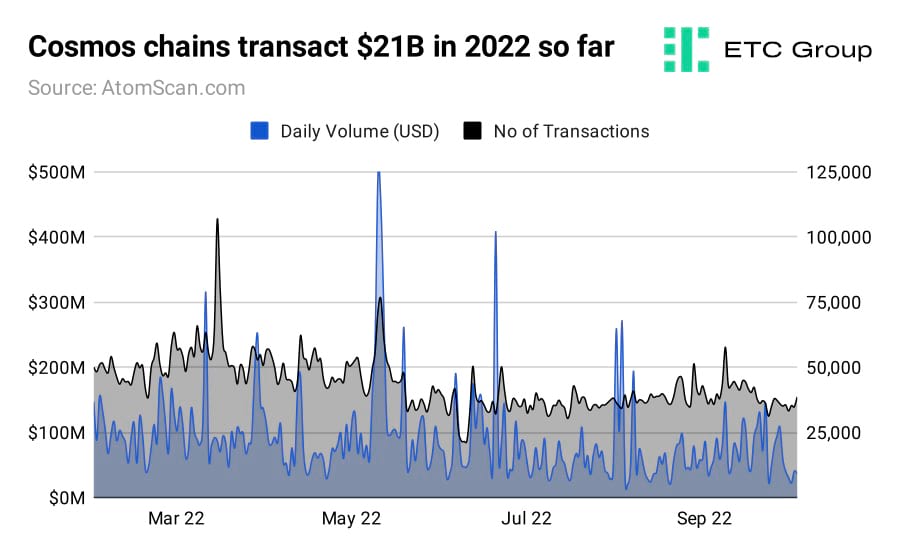
Cosmos developers introduced a new whitepaper on 26 September at the Cosmoverse conference in Medellin, Columbia. It puts forward a new role for ATOM tokens as the preferred collateral within the Cosmos network.
The paper also brings to light the concept of a new issuance schedule for liquid staking, where after a 36 month transition period, ATOM issuance will be reduced to a constant amount per month.
Cosmos currently relies on three key assets to function.
- The Tendermint Core consensus algorithm;
- The Cosmos Hub mainnet, which launched in March 2019; and
- IBC ( Inter-Blockchain Communication), a set of code that allows the different blockchains in the ecosystem to communicate with the Cosmos Hub.
- One key extra value proposition comes from the Cosmos SDK (software development kit).
It can take months or even years to build a blockchain network from scratch. Cosmos instead offers blockchain developers prebuilt modules through this SDK, which is an open source framework which includes a vast array of toolkits, plugins and code libraries, so that they can achieve a functioning product in a matter of weeks.
Now that all of the above has been achieved, alongside the sharpening of new technologies to secure economic scaling (Interchain Security and Liquid Staking), Cosmos developers say “the original vision of the Hub has been fulfilled”.
The new whitepaper
marks the transition to the next phase of the Cosmos Hub as an infrastructure service platform,
they add. Essentially, it is now time for a new challenge and new goals to aspire to so Cosmos Hub can be a leading destination for emerging blockchains to set up shop.
In a sign of the times, decentralised exchange dydx announced earlier this year that for its fourth iteration (V4) it would build its own blockchain on Cosmos using the Cosmos SDK and Tendermint consensus protocol, instead of remaining on Ethereum.
dYdX is one of the largest decentralised exchanges (DEXs) in the entire blockchain finance ecosystem. Launched in April 2019 on Ethereum, it offers lending, borrowing perpetual futures contracts, alongside margin and spot trading.
The platform is consistently rated in the top two globally for trading volume, alongside Uniswap (UNI). As of 5 October, it was handling $535m in daily volume.
Its move to Cosmos is a signal that popular dapps and their users cannot wait forever while Ethereum figures out its transaction fee and scaling structure.
As dYdX developers noted:
Cosmos is a technology that makes it relatively easy to create a standalone blockchain with strong cross-chain capabilities.
The Hub was the only Cosmos chain when it launched in 2019 but its code has since been used as a template by dozens of other interconnected blockchains, each designed for a specific use case. Users can stake ATOM on it to secure the network but the token has lacked additional functionality to date.
In the past, the Cosmos community has resisted changes to the Hub's code that may be detrimental to its role as a place for other chains to build on.
At present, speculators tend to trade ATOM like an index of the Cosmos ecosystem as a whole. But now Cosmos Hub intends to level up, analysts can see its value proposition soar along with the changes.
Markets
Some positive sentiment has started to trickle back into digital assets over the past fortnight. The total digital asset market cap remains under a trillion dollars. Bitcoin has recovered by close to 5% over the last two weeks with its price sandwiched between a key support level of $18,500 and resistance level of $20,000.
Ethereum has plugged the hole that saw it lose about a fifth of its value in the days following the sell-off that accompanied the Merge on 15 September. Its price has bounced by 4% since the last edition of Crypto Minutes was published.
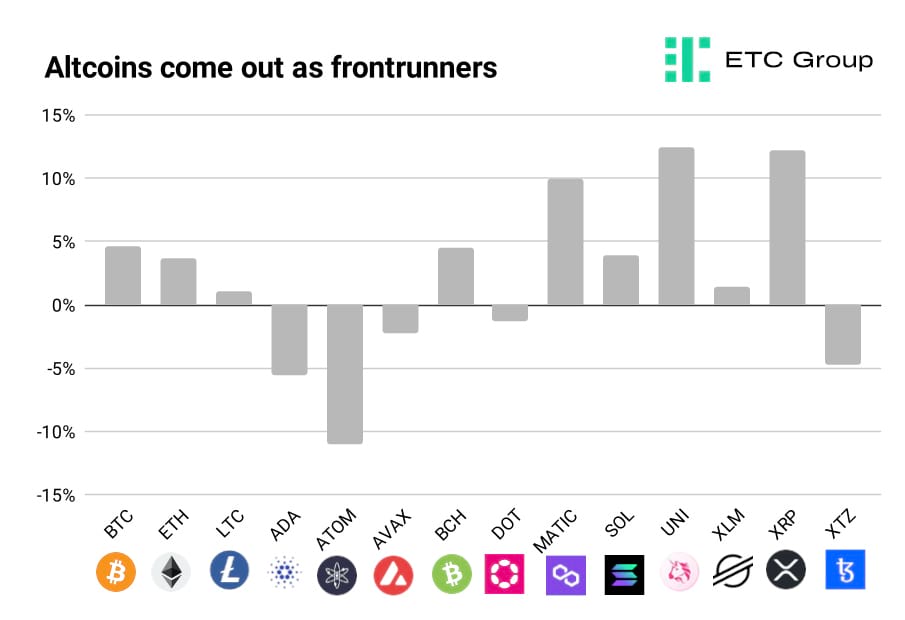
Certainly signs that crypto has started to decouple from equities has produced a positive shift in investor appetite.
And while the largest digital assets witnessed single digit percent uplifts, altcoins further down the market cap table have been the main beneficiaries.
Ethereum Layer 2 tech Polygon (MATIC) added 10% over the last two weeks, decentralised exchange token Uniswap added 12% and XRP, on suggestions that its two-year SEC securities case is coming to a close, climbed by the same amount.
AVVISO IMPORTANTE:
Questo articolo non costituisce consulenza finanziaria, né rappresenta un'offerta o un invito all'acquisto di prodotti finanziari. Questo articolo è solo a scopo informativo generale, e non vi è alcuna assicurazione o garanzia esplicita o implicita sulla correttezza, accuratezza, completezza o correttezza di questo articolo o delle opinioni in esso contenute. Si consiglia di non fare affidamento sulla correttezza, accuratezza, completezza o correttezza di questo articolo o delle opinioni in esso contenute. Si prega di notare che questo articolo non costituisce né consulenza finanziaria né un'offerta o un invito all'acquisizione di prodotti finanziari o criptovalute.
PRIMA DI INVESTIRE IN CRYPTO ETP, GLI INVESTITORI POTENZIALI DOVREBBERO CONSIDERARE QUANTO SEGUE:
Gli investitori potenziali dovrebbero cercare consulenza indipendente e prendere in considerazione le informazioni rilevanti contenute nel prospetto base e nelle condizioni finali degli ETP, in particolare i fattori di rischio menzionati in essi. Il capitale investito è a rischio, e le perdite fino all'importo investito sono possibili. Il prodotto è soggetto a un rischio controparte intrinseco nei confronti dell'emittente degli ETP e può subire perdite fino a una perdita totale se l'emittente non adempie ai suoi obblighi contrattuali. La struttura legale degli ETP è equivalente a quella di un titolo di debito. Gli ETP sono trattati come altri strumenti finanziari.


